Promoting open, inclusive, transparent, and traceable science requires that scientists revamp the ways in which we acknowledge all manner of contributions to research.
data management
Open and Fair Data in Tropical Forests
People who gather ground data on tropical forests are highly disadvantaged compared to the users of such data. A new paper suggests long-term collaborations as a path forward.
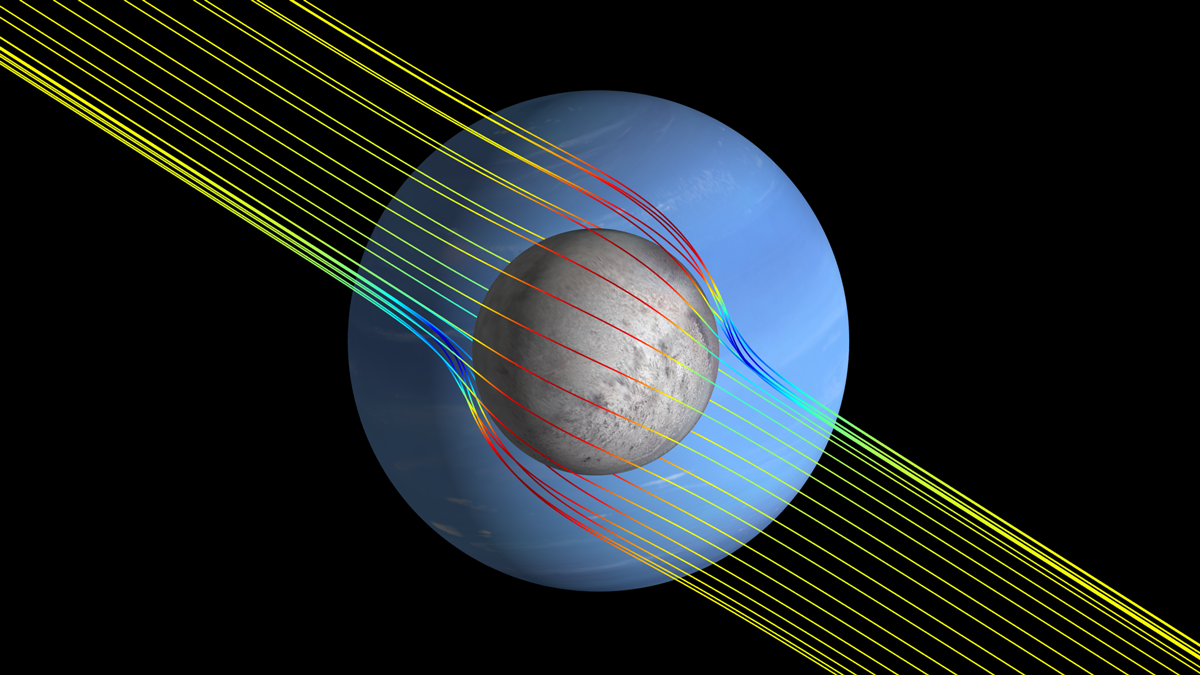
Encontrando los océanos ocultos de las lunas usando campos magnéticos inducidos
Un análisis de componentes principales de modelos especulativos puede predecir con más seguridad que las técnicas anteriores la p^ppresencia de un océano subsuperficial en un objeto planetario.
Diagnosing Neptune’s Chilly Summer
A pandemic project analyzing a trove of infrared images revealed an unexplained phenomenon taking place in Neptune’s atmosphere.
A New Index to Quantify River Fragmentation
Researchers have developed a new analysis based on a river’s catchment area as opposed its length.
A Sharper Look at the World’s Rivers and Catchments
Digital hydrographic maps have transformed global environmental studies and resource management. A major database update will provide even clearer and more complete views of Earth’s waterways.
A Puzzle Mat for Assembling Colombia’s Geologic History
A new database compiles all the available pieces of information about Colombia’s geochronology, offering scientists a consistent framework in which to view and study the data in a broader context.
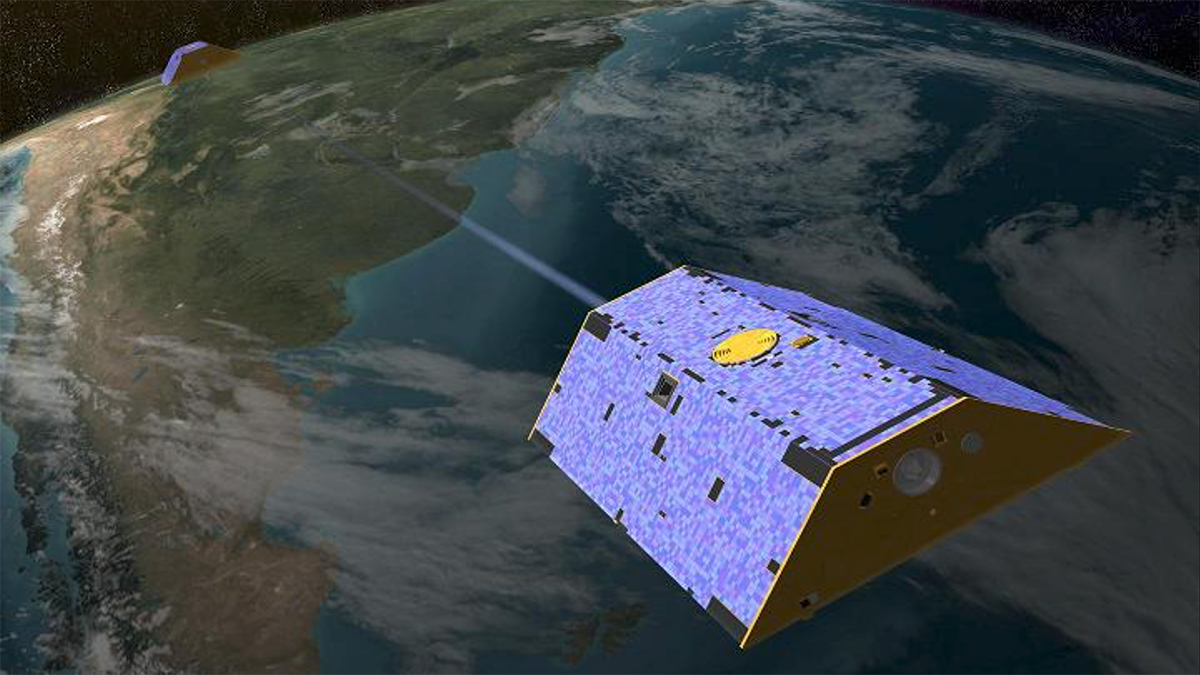
Fresh Approaches to Processing GRACE Data
Two studies showcase new methods for analyzing GRACE data that better match the land surface, producing clearer estimates of mass variations.
Tree Carbon Data That Ring True
An international group of researchers may have found a way to better account for carbon storage in forests.