The 2021 Nobel Prize in Physics was awarded for climate modeling and for the discovery of multifractals to describe intermittency and the scaling dynamics of climate variables, including extremes.
Modeling
A Drier or Wetter Future for Southwestern North America?
Bhattacharya et al. present evidence that expansion of the North American Monsoon explains a wetter southwest in the mid-Pliocene and suggest this mechanism can explain current monsoon variations.
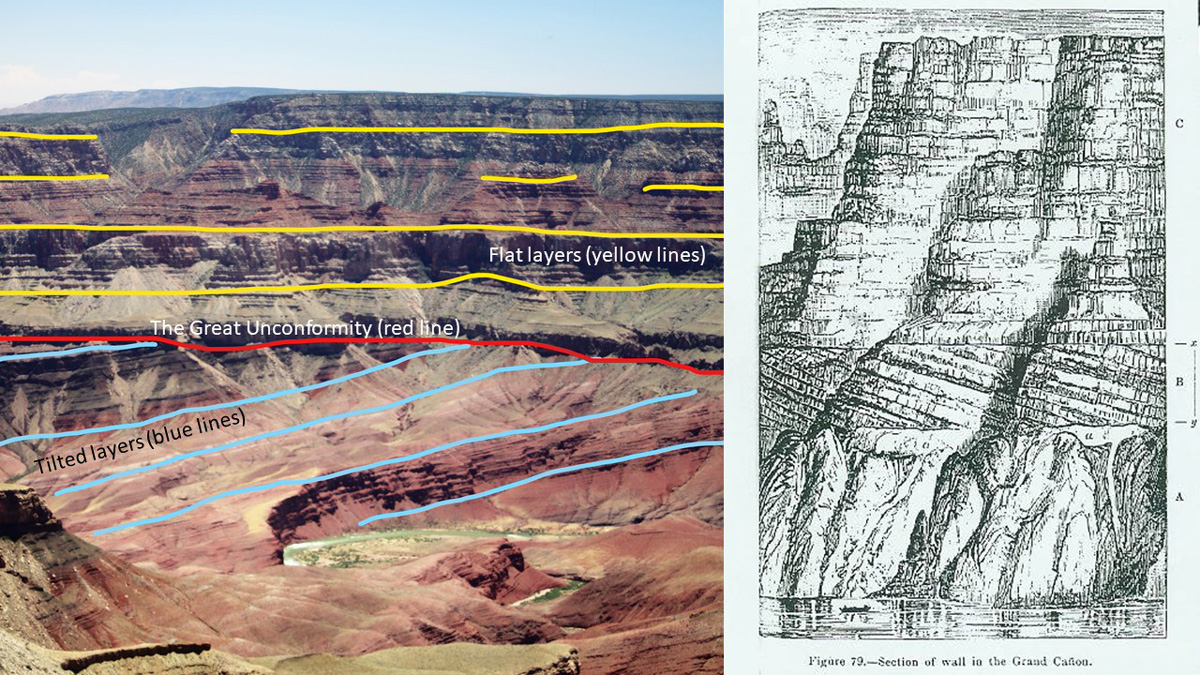
The Great Unconformity or Great Unconformities?
Some scientists think the Great Unconformity was caused by Snowball Earth’s glaciations. Recent work suggests these phenomena might not be related.
New Tectonic Plate Model Could Improve Earthquake Risk Assessment
A new model of tectonic plates in New Zealand may identify areas of increased earthquake likelihood.
Groundwater Replenishes Much Faster Than Scientists Previously Thought
A new climate-based model indicates that scientists may be underestimating groundwater’s importance in sustaining streams and plant life.
Outsourcing the Work of Industrial Climate Science
Climate science is increasingly structured in ways that subcontract repetitive activities to graduate students. Here, early career researchers raise the issue and explore some tradeoffs.
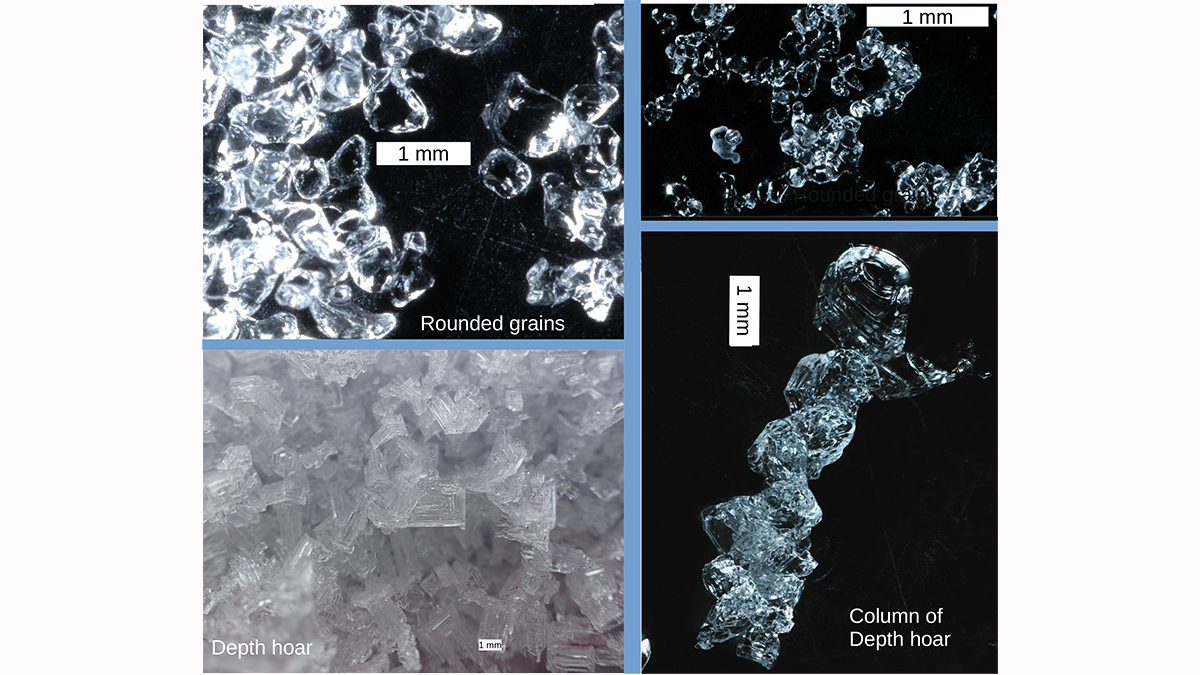
Measuring the Microstructure of Snow from Space
There is more to snow than flakes. Microwave measurements are shown to be capable of illuminating the microstructure of snow in ways that will improve our ability to monitor snow fields from space.
Protecting Poor Neighborhoods from Landslide Risk
As low-income, informal settlements bloom in the tropics, their risk of landslides increases. A new modeling tool incorporates urbanization factors to protect the region’s poorest neighborhoods.
Callisto’s H Corona: Offspring of the Surface or the Atmosphere?
The mostly unknown Callisto’s H corona is created by a global tenuous H2 atmosphere and not by surface water as previously believed, providing the first evidence for H2 in Callisto’s atmosphere.
Linking African Winds to Atlantic Storms
Simulations suggest that waves in the atmosphere above northern Africa influence the intensity, timing, and location of formation of Atlantic tropical cyclones.