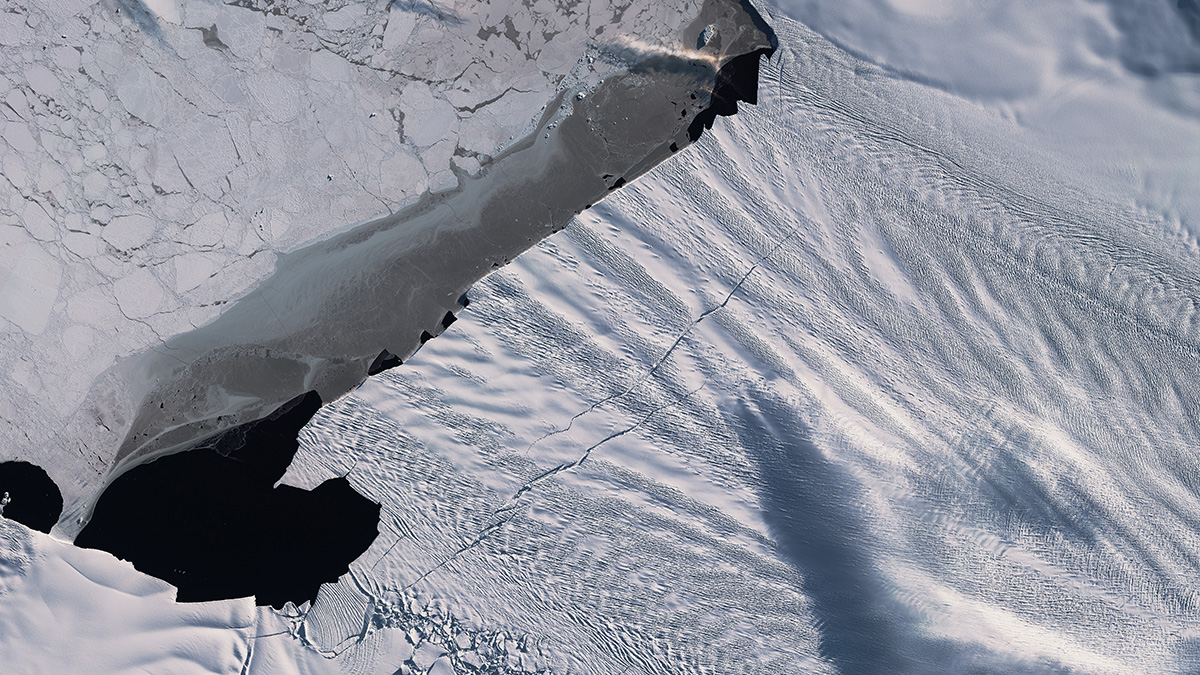
New research shows that increased calving from West Antarctica’s Pine Island Ice Shelf will likely drive increased circulation of warm water—and melting—below the ice.
Modeling
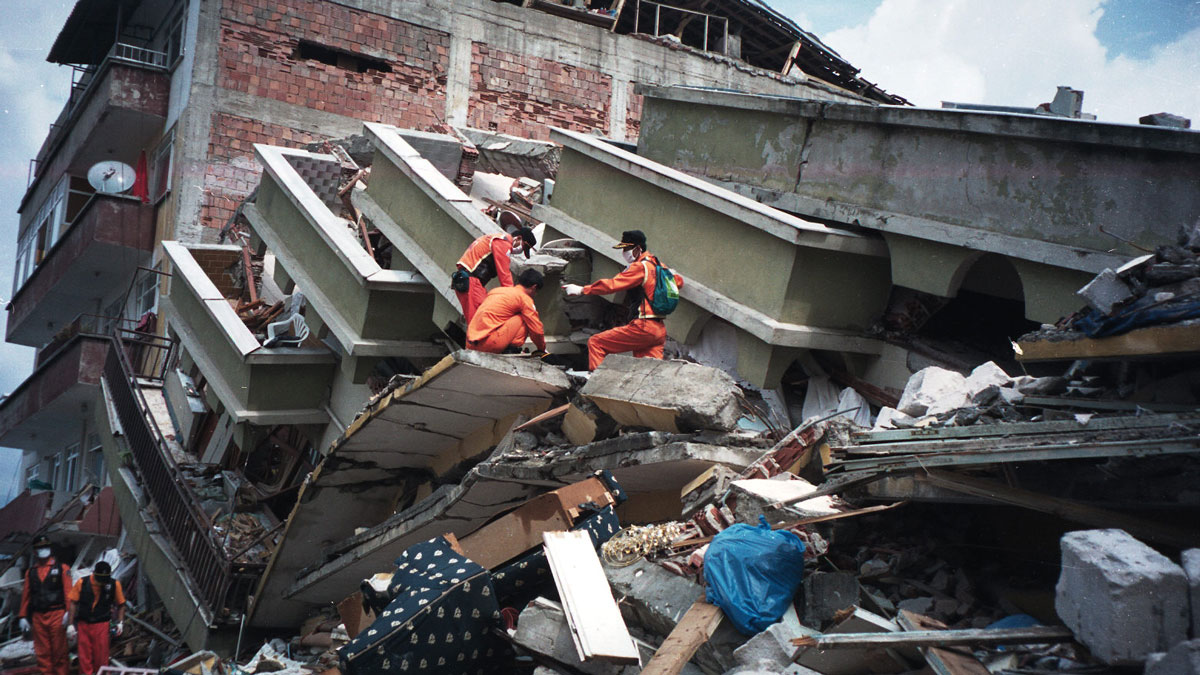
¿Tienen los terremotos y las placas tectónicas una relación bidireccional?
Un terremoto catastrófico en Turquía que sucedió en 1999 cambió el movimiento de la placa de Anatolia, según un estudio que podría modificar los fundamentos de modelamiento de los terremotos.
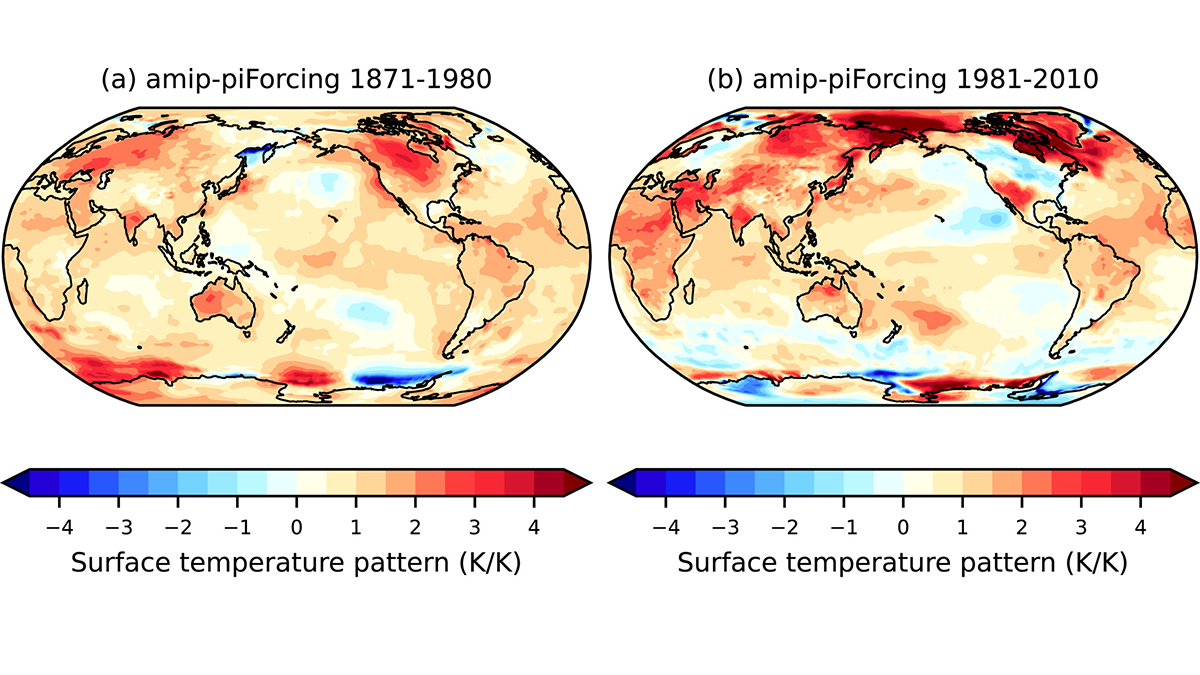
A Dilemma About Radiative Climate Feedback in Recent Decades
Given the unambiguous climate warming in recent decades, is it possible to infer radiative climate feedback from modern satellite measurements of the energy budget of the Earth?
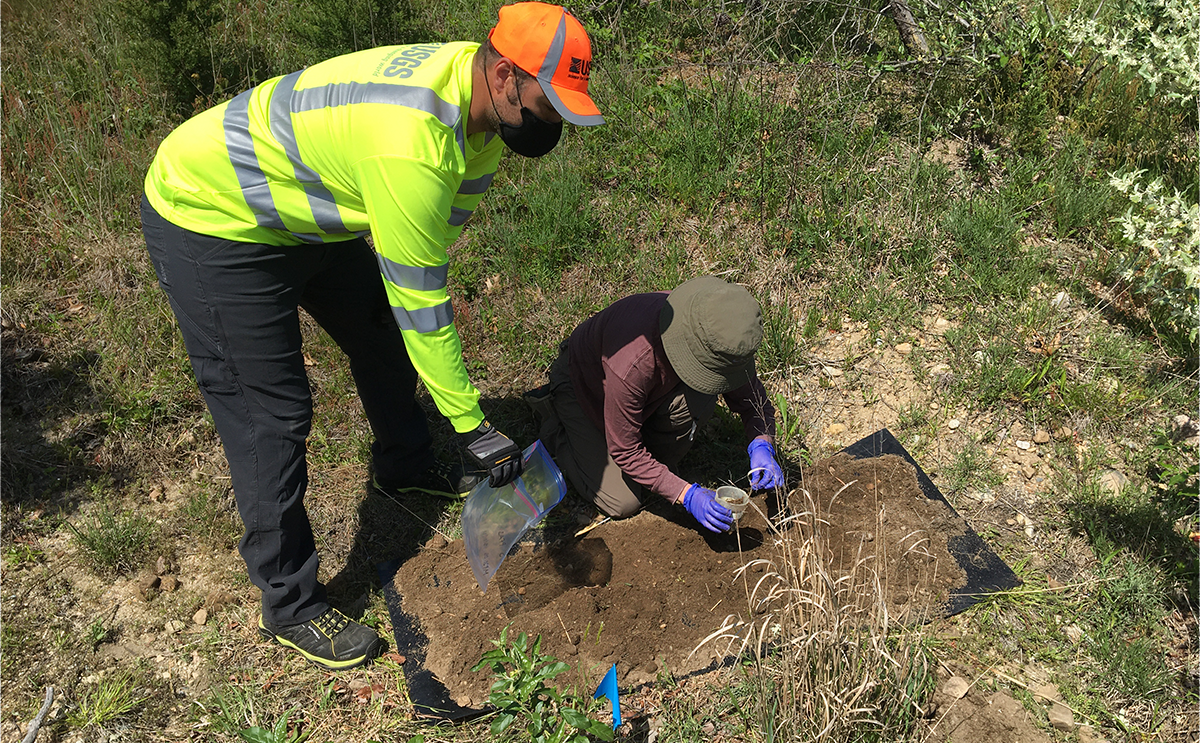
Widespread “Forever Chemicals” in Subsurface Environments
Massive use of materials containing per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in commercial and industrial sectors has led to their widespread occurrence in subsurface environments.
When Projecting Coastal Resilience, Sediment Compaction Is Key
The addition of new sediment helps build up lowland environments like deltas and marshes, but it also compacts materials beneath it—a vital, but often overlooked, factor in landscape evolution studies.
Satellites Can Accurately Take Earth’s Temperature
Satellite-based measurements of land surface temperature may prove to be an essential pairing with near-surface air temperatures to understand global warming and cooling trends.
Substantial Advance Towards a Global Coastal Carbon Model
First simulations of a new biogeochemistry-circulation coastal grid refinement demonstrate seamless inclusion of small-scale coastal processes in a state-of-the-art Earth system model.
Massive Stars May Commit Grand Theft Planet
New simulations show that planets around young, massive stars may have been captured or stolen rather than homegrown.
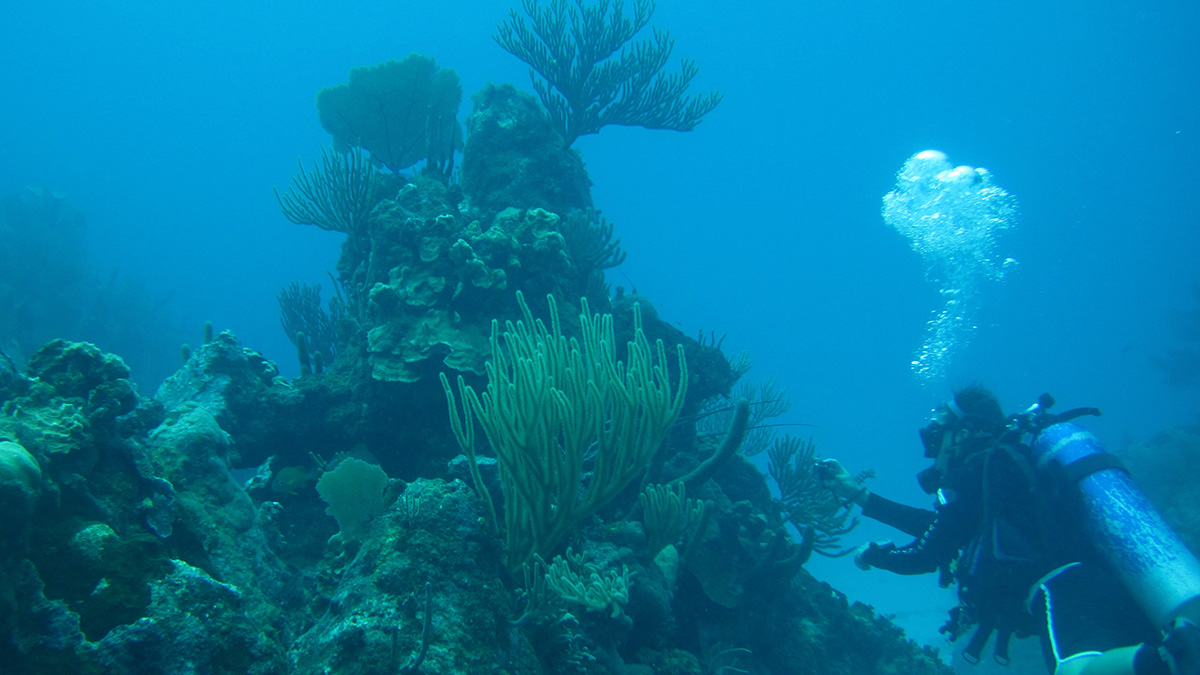
Unchecked Ocean Warming Threatens Many Gulf and Caribbean Corals
Gulf of Mexico and Caribbean sea surface temperatures could surpass coral bleaching thresholds in the region as soon as 2050, motivating the need for prompt mitigation, researchers say.
Variability of ENSO Forecast Skill Over the 20th Century
El Niño Southern Oscillation (ENSO) predictability is examined in a new global coupled retrospective forecast ensemble for the 20th Century.