By incorporating human systems, scientists are modeling geohazards with equity in mind.
earthquakes
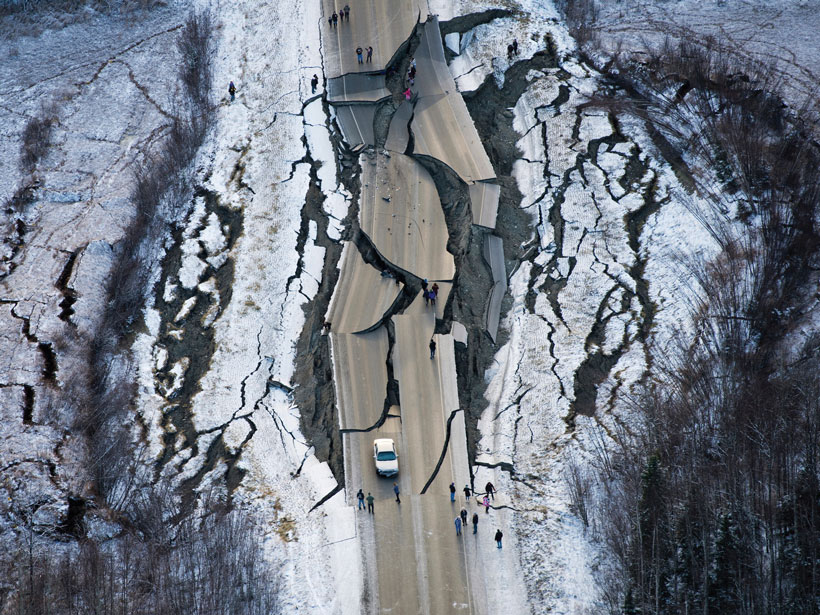
Amateur Radio Operators Help Fill Earthquake Donut Holes
Ham radio networks gear up to provide real-time, on-the-ground information about earthquake shaking and damage when other communication pathways are knocked out of commission.
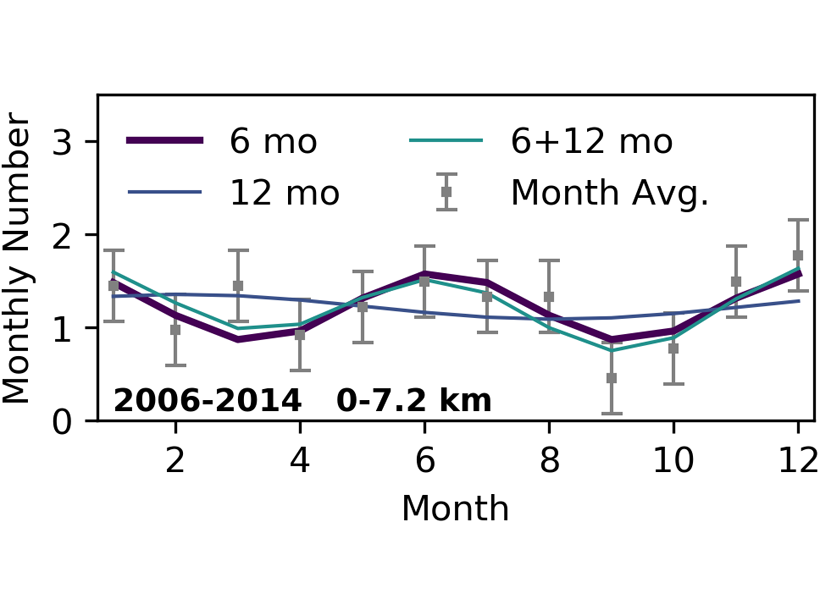
Why are Earthquakes on the San Andreas Seasonally Modulated?
There is growing evidence that some earthquakes occur seasonally but also that water loading cannot explain these observations.
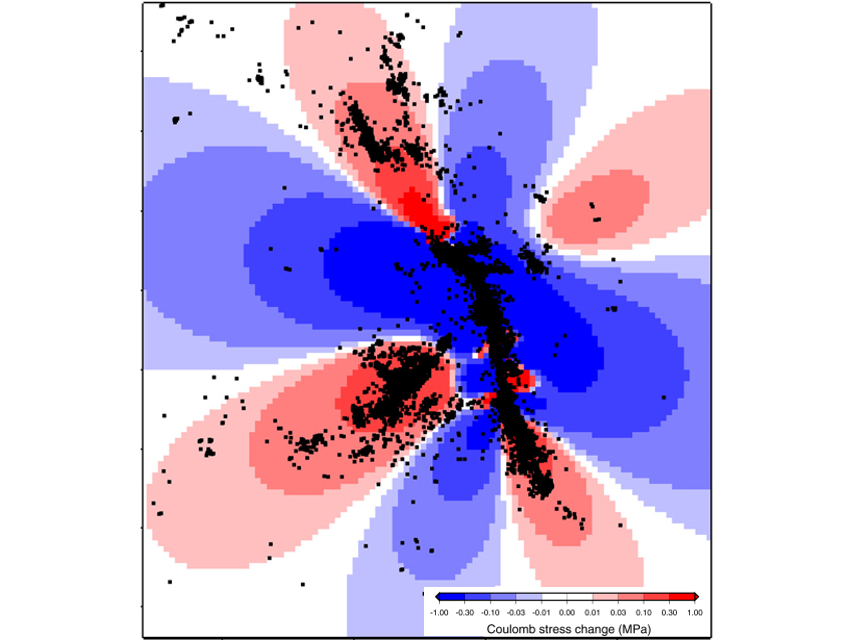
The Failure of Physics-Based Earthquake Forecasting Models
Spatial clustering of aftershocks explains why simple statistical models often outperform complex physics‐based earthquake forecasting models even if the physical mechanisms are correctly modeled.
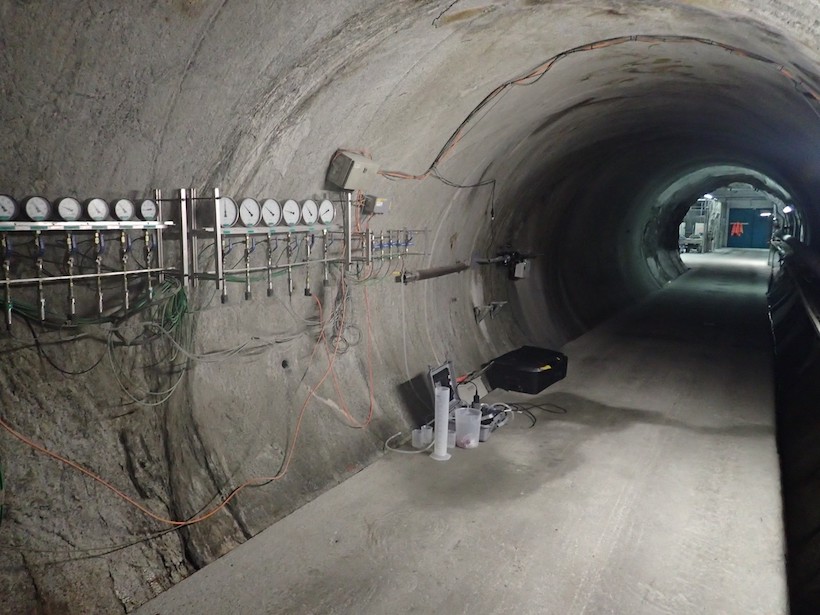
Earthquakes Can Acidify Groundwater
Fracturing during microearthquakes can cause groundwater pH drops. The change is temporary but can be equivalent to the difference between water and vinegar.
Using Earthquake Forensics to Study Subduction from Space
Researchers combined satellite geodetic measurements of surface motion with a new geophysical data inversion method to probe the Chilean subduction zone in the wake of the 2010 Maule earthquake.
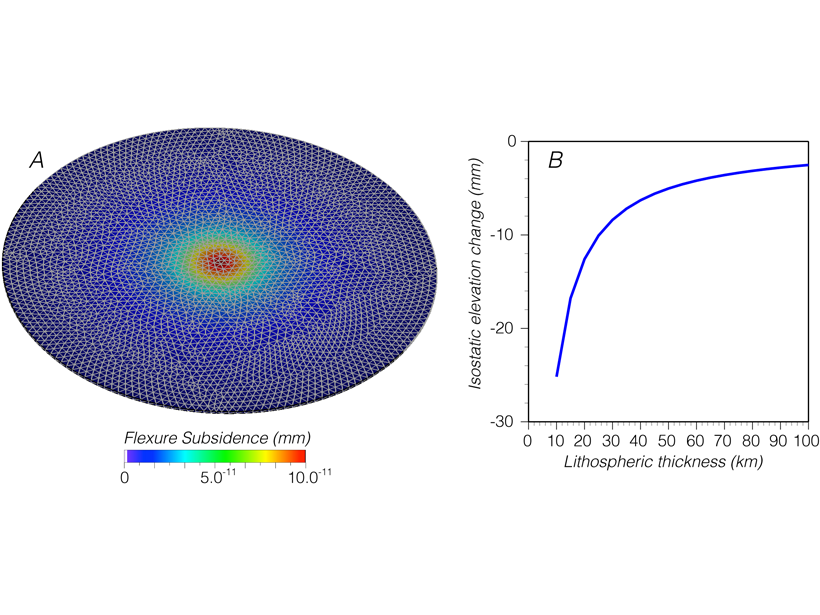
Going Down: How Do Cities Carry That Weight?
Calculations show that the added weight of growing cities can lead to tens of millimeters of subsidence, an effect that needs to be considered for coastal cities under threat by sea-level rise.
Researchers Produce First Artificial Icequakes
Laboratory experiments show similarities between glacier beds and tectonic faults.
Predicting the Next Big Frost Quake
Frost quakes occur in boreal regions when rapidly expanding ice underground causes frozen soils to fracture. A recent frost quake in Finland has given scientists a rare look into how they form.
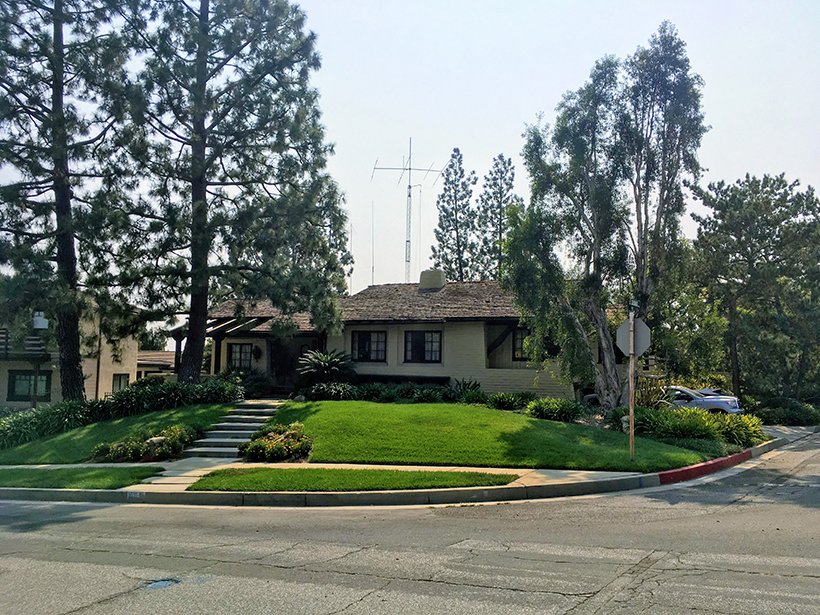
Wildfires Threaten West Coast’s Seismic Network
A dense seismic network keeps vigil over the western United States, sensing quakes soon after they begin so people nearby can brace themselves. How do wildfires affect these guardians of the West Coast?