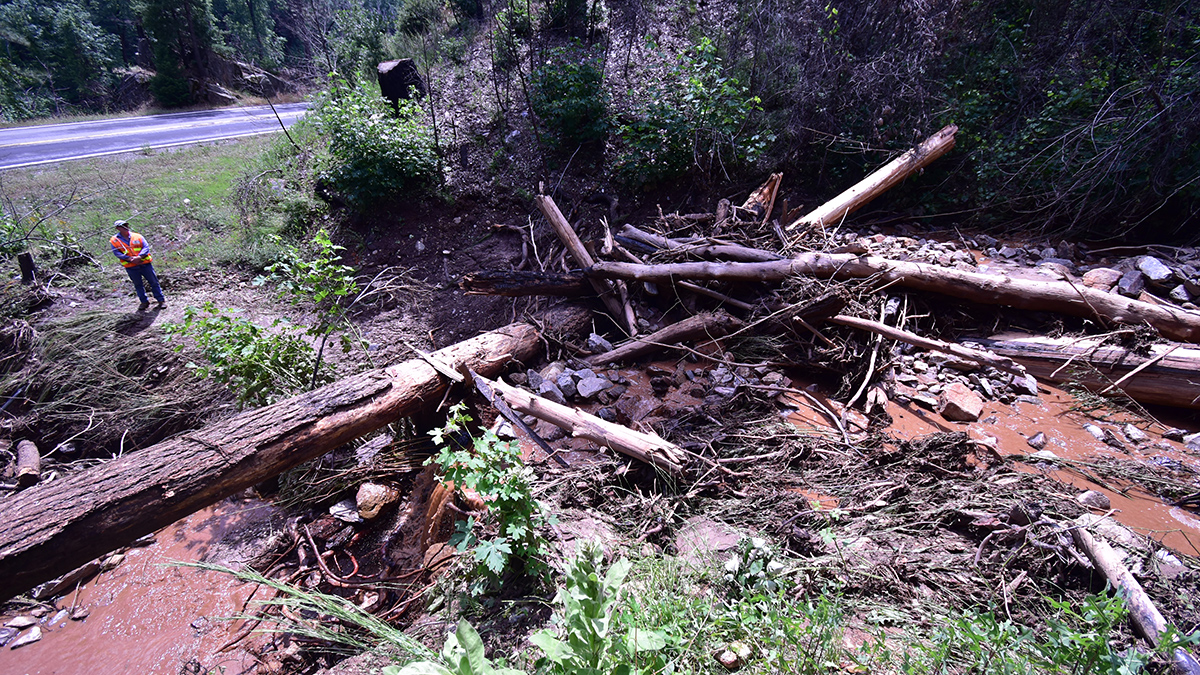
California geologists are improving their understanding and forecasting of which slopes in wildfire-burned areas might fail during heavy rainstorms.
Earth science
Ostrich Eggshells Trace Namaqualand’s Ancient Rain
The plant-based nitrogen eaten by ostriches and stored in their eggshells was measured by researchers 20,000 years later.
Ecosystem Observations from Every Angle
Proximal remote sensing provides a bridge between ecosystem flux data at Earth’s surface and optical data from satellite sensors, improving our grasp of feedbacks between terrestrial ecosystems and climate.
Weather and Watershed Forecasting Make for Dam Smart Water Use
Using weather forecasts in reservoir management improves decisions about water supplies. Now researchers are studying the hydrology around reservoirs to help apply this strategy nationwide.
Beavers Have Engineered Ecosystems in the Tetons for Millennia
Analysis of lake sediment in Grand Teton National Park is helping piece together ecosystem history, with helpful implications for land managers today.
Another Record-Breaking Year in the Arctic Amplifies Calls for More Data
A downward spiral of the Arctic’s ecological health and climatic conditions continued in 2023, causing problems for people, plants, and animals, according to a new NOAA report.
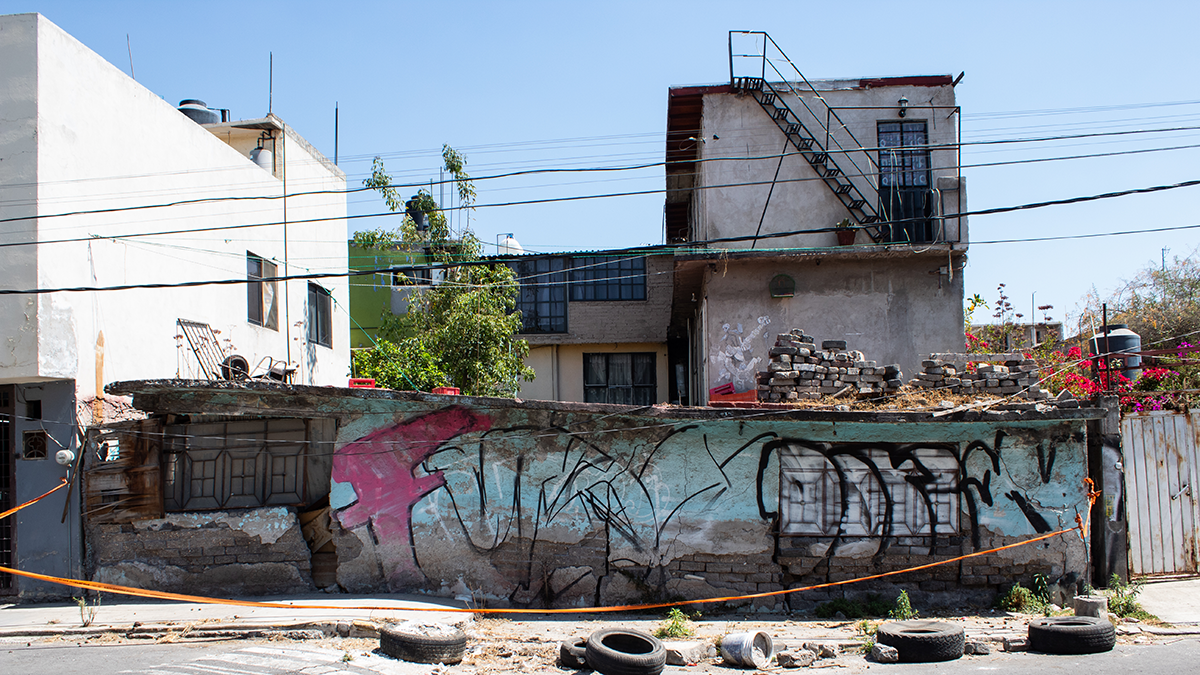
La extracción de agua subterránea está causando el hundimiento de la CDMX
Investigadores aseguran que saber cuánta agua está siendo extraída es crucial para resolver la crisis de infraestructura y de abastecimiento de agua en la capital.
Satellites Map Environmental Vulnerabilities in U.S. Prisons
Geoscientists are using remote sensing to gather data on risks including increased exposure to air and soil pollution, excessive heat, wildfire, and flooding.
Ocean Vessels May Trigger Lightning Strikes
Previous research indicated aerosols in ship exhaust could enhance lightning. New research indicates the ships themselves may be to blame as well.
Mammal Droppings Preserve Human and Climate History on the Tibetan Plateau
Geochemical signatures in sediment, which includes organic molecules from human and animal poop, help scientists track the rise and fall of the Tibetan Empire.